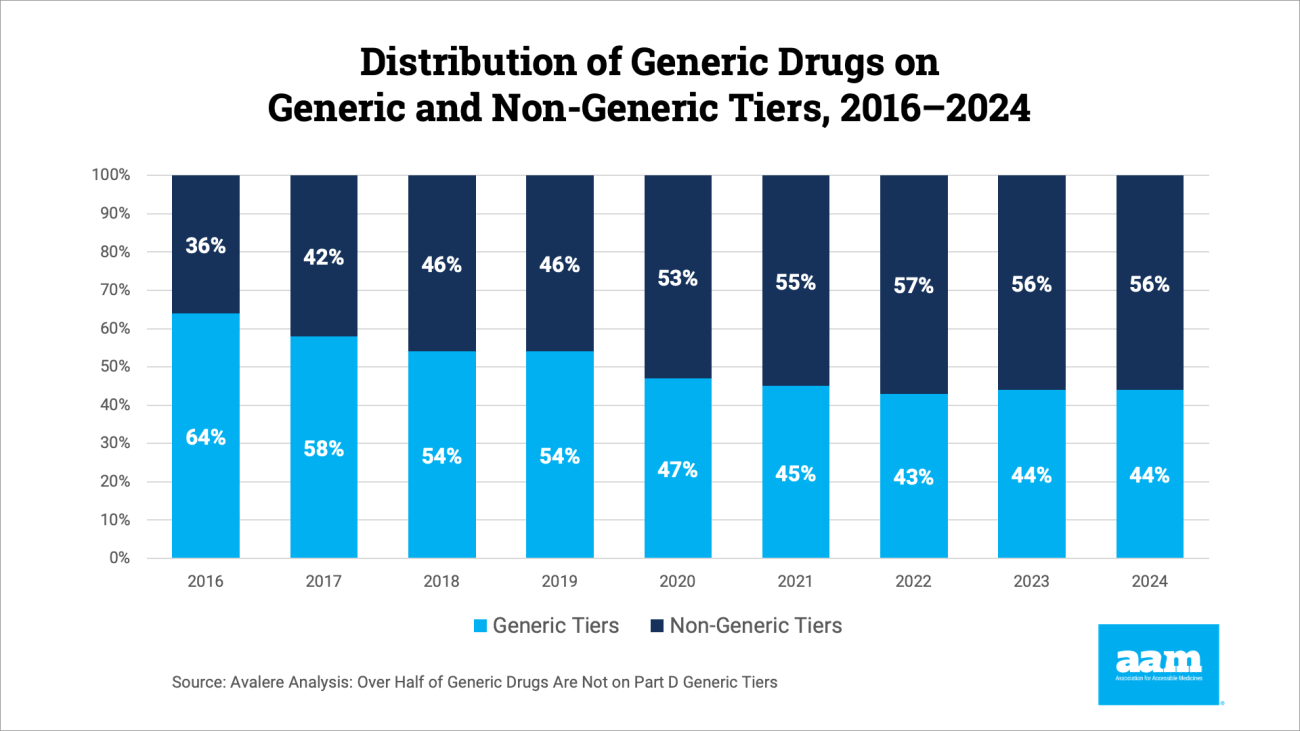
Avalere Analysis finds that fewer than half of all generic drugs are on generic formulary tiers
WASHINGTON (February 20, 2024) — The Association for Accessible Medicines, the leading trade association for generic and biosimilar manufacturers, commented on an analysis released today by Avalere showing that Medicare plans increase patient costs for generic medicines.
“Avalere's analysis demonstrates that fewer than half of all generic drugs are on generic formulary tiers,” said David Gaugh, Interim President & CEO of AAM. “Medicare Part D Plans continue to deny patients the full value of low-cost generic drugs. Plans are profiting from patients using generic drugs through higher copays and placement on brand formulary tiers, even as generic prices continue to fall. AAM encourages the Administration and Congress to ensure that Medicare beneficiaries receive the full value of low-cost generics.”
Avalere has analyzed Plan D sponsors and the distribution of generic prescription drugs on the various tiers from 2016 to 2024. They found sponsors placed a higher proportion of covered generic drugs on non-generic tiers over time. The analysis also found that a higher percentage of generic medicines have been placed on non-preferred tiers since 2016, and grew 20 percent, from 36% in 2016 to 56% in 2024.
In the last ten years, the use of generic drugs has saved patients and the U.S. healthcare system almost $3 trillion dollars. Medicare patients deserve the full benefit of the savings provided by generics and biosimilars.
In Medicare Part D, medicines are covered on formulary tiers. A drug in a lower tier will have a lower copay than a drug in a higher tier. For example, on average a plan may charge as low as $0 for preferred generics on Tier 1, $5 for generics on Tier 2, $42 for products on Tier 3 and a percentage of the list price for drugs on Tiers 4 and 5. The intent is to encourage seniors to use the lowest cost option possible. Because generic drugs are significantly less expensive than their brand counterparts, they have historically been placed on the lowest tier. In recent years, as prices for generic medicines continue to fall, many Medicare Part D plans continue to place generics on higher tiers with higher copays. This forces seniors to pay more for lower-cost generic medications, and the copay is often significantly more than the cost of the medication.
For media inquiries, contact the Communications department at media@accessiblemeds.org.
About AAM
The Association for Accessible Medicines, your generics and biosimilars industry, is driven by the belief that access to safe, quality, effective medicine has a tremendous impact on a person’s life and the world around them. Generic and biosimilar medicines improve people’s lives, improving society and the economy in turn. AAM represents the manufacturers of finished generic pharmaceuticals and biosimilars, manufacturers of bulk pharmaceutical chemicals, and suppliers of other goods and services to the generic industry. Generic pharmaceuticals are 90 percent of prescriptions dispensed in the U.S. but only 17.5 percent of total drug spending.
About the Biosimilars Council
The Biosimilars Council, a division of the Association for Accessible Medicines (AAM), works to ensure a positive environment for patient access to biosimilar medicines. The Biosimilars Council is a leading source for information about the safety and efficacy of more affordable alternatives to costly brand biologic medicines. Areas of focus include public and health expert education, strategic partnerships, government affairs, legal affairs and regulatory policy. More information is available at www.biosimilarscouncil.org.